PANDORA Pixel-wise Attention Dissolution and Latent Guidance for Zero-Shot Object Removal
Pixel-wise Attention Dissolution and Latent Guidance for Zero-Shot Object Removal
Demo Video
Abstract
Removing objects from natural images remains a formidable challenge, often hindered by the inability to synthesize semantically appropriate content in the foreground while preserving background integrity. Existing methods often rely on fine-tuning, prompt engineering, or inference-time optimization, yet still struggle to maintain texture consistency, produce rigid or unnatural results, lack precise foreground-background disentanglement, and fail to flexibly handle multiple objects—ultimately limiting their scalability and practical applicability. In this paper, we propose a zero-shot object removal framework that operates directly on pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models—requiring no fine-tuning, no prompts, and no optimization. At the core is our Pixel-wise Attention Dissolution, which performs fine-grained, pixel-wise dissolution of object information by nullifying the most correlated keys for each masked pixel. This operation causes the object to vanish from the self-attention flow, allowing the coherent background context to seamlessly dominate the reconstruction. To complement this, we introduce Localized Attentional Disentanglement Guidance, which steers the denoising process toward latent manifolds that favor clean object removal. Together, Pixel-wise Attention Dissolution and Localized Attentional Disentanglement Guidance enable precise, non-rigid, scalable, and prompt-free multi-object erasure in a single pass. Experiments show our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods even with fine-tuned and prompt-guided baselines in both visual fidelity and semantic plausibility.
Object Removal
We propose a zero-shot object removal framework that operates directly on pre-trained diffusion models in a single pass, without any fine-tuning, prompt engineering, or inference-time optimization, thus fully leveraging their latent generative capacity for inpainting
🖱️Click to see results
⏱️Processing takes ~10 seconds - please be patient!
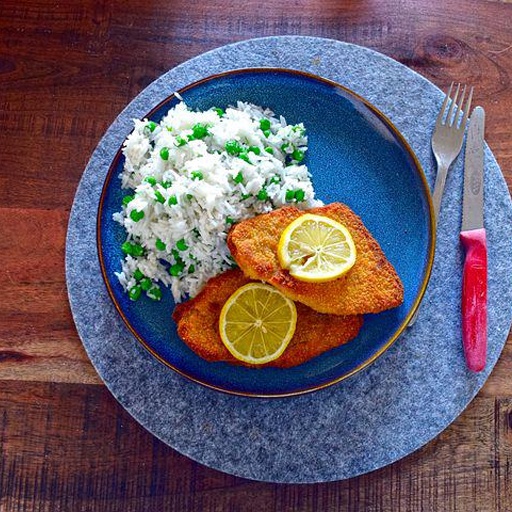












Approach
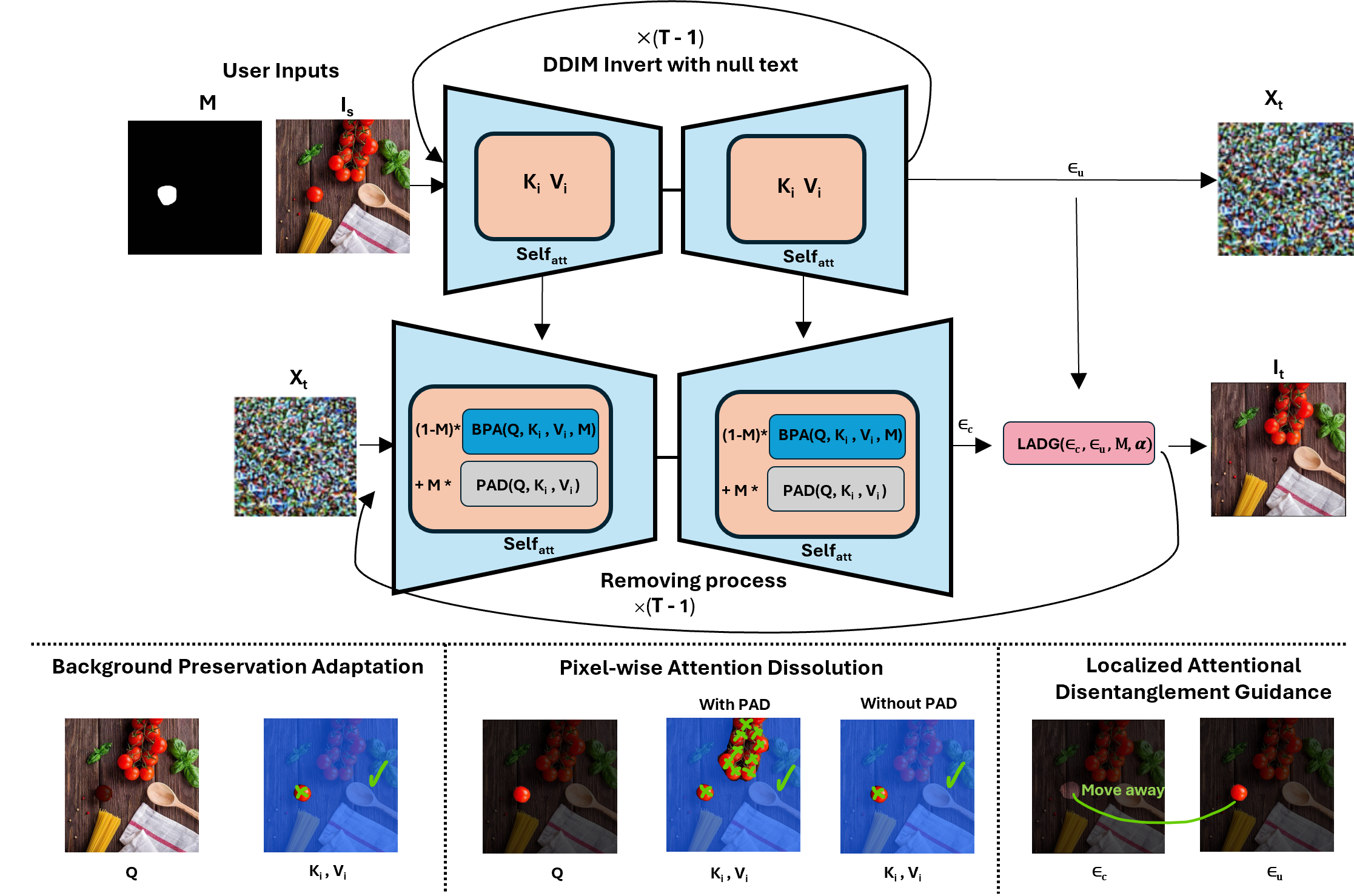
Our framework performs zero-shot object removal directly on a pre-trained diffusion model. Given an input image Is and a binary mask M specifying the target objects, the model produces an edited image It where the masked regions are erased and seamlessly reconstructed with contextually consistent background. The process begins with latent inversion to map the input image into the noise space while preserving unaffected regions in the denoising process. We then apply Pixel-wise Attention Dissolution (PAD) to disconnect masked query pixels from their most correlated keys, effectively dissolving object information at the attention level. Next, Localized Attentional Disentanglement Guidance (LADG) steers the denoising trajectory in latent space away from the object regions, refining the reconstruction to suppress residual artifacts.
Together, PAD and LADG enable precise, pixel-level control for single- and multi-object removal in a single forward pass, without any fine-tuning, prompt engineering, or inference-time optimization.
Qualitative Comparison
🔬Qualitative comparison on various object removal scenarios📊From left to right: original image with a mask, and results from different methods
Single-Object Removal
Top two rows
Multi-Object Cases
Middle two rows
Mass-Similar Objects
Bottom two rows
⚡Zero-shot methods shown in the last four columns, with the last two columns showing our PANDORA method

Quantitative Comparison
| Method | Text | FID↓ | LPIPS↓ | MSE↓ | CLIP score↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-tuning-based methods (SD 2.1 backbone, except LaMa) | |||||
| PowerPaint | ✔ | 22.81 | 0.1322 | 0.0104 | 24.15 |
| LaMa | ✘ | 0.71 | 0.0012 | 0.0001 | 24.5 |
| SD2-Inpaint | ✘ | 17.93 | 0.1106 | 0.0073 | 24.06 |
| SD2-Inpaint-wprompt | ✔ | 18.01 | 0.1098 | 0.0072 | 24.32 |
| Zero-shot methods (no retraining, SD 2.1 backbone) | |||||
| CPAM | ✘ | 25.25 | 0.0953 | 0.0048 | 24.49 |
| PANDORA w/o PAD (Ours) | ✘ | 27.3 | 0.0985 | 0.005 | 24.58 |
| PANDORA w/o LADG (Ours) | ✘ | 30.8 | 0.1007 | 0.0055 | 24.65 |
| PANDORA (Ours) | ✘ | 35.1 | 0.1064 | 0.0059 | 24.69 |
| Zero-shot methods (no retraining, SD 1.5 backbone) | |||||
| CPAM | ✘ | 29.54 | 0.1564 | 0.0138 | 24.32 |
| Attentive Eraser | ✘ | 118.09 | 0.2567 | 0.027 | 24.42 |
| PANDORA w/o PAD (Ours) | ✘ | 35.59 | 0.1702 | 0.0156 | 24.4 |
| PANDORA w/o LADG (Ours) | ✘ | 42.17 | 0.1844 | 0.0171 | 24.55 |
| PANDORA (Ours) | ✘ | 44.98 | 0.1895 | 0.0184 | 24.57 |
Quantitative comparison of fine-tuned and zero-shot object removal methods averaged across all dataset types. PANDORA consistently achieves the best object removal quality with competitive background realism, without any retraining or textual prompts, demonstrating strong generalization across both Stable Diffusion v1.5 and v2.1 backbones. Removing LADG slightly reduces removal quality, while removing PAD causes a significant degradation.
Acknowledgment
Funding and GPU Support
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under Grant Number 102.05-2023.31. This research used the GPUs provided by the Intelligent Systems Lab at the Faculty of Information Technology, University of Science, VNU-HCM.
User Study Participants
We extend our heartfelt gratitude to all participants who took part in our comprehensive user study. Your valuable time, thoughtful feedback, and detailed evaluations were instrumental in validating the effectiveness and usability of our PANDORA framework. Your insights helped us understand the practical impact of our zero-shot object removal approach and provided crucial evidence of its superiority over existing methods.
Website Design Inspiration
This website design is inspired by ObjectDrop. We thank the authors for their excellent work and creative design approach.
Demo Design Inspiration
Our Gradio demo design is inspired by MimicBrush. We thank the authors for their excellent work and creative design approach.